| 
|
Arrays with multiple dimensions may be declared and used in Java. Two-dimensional (2D) arrays are useful when data can be represented by a grid of fixed size. 2D arrays are often used to represent tables, images, and game boards. Checkers, chess, tic-tac-toe, crosswords and mazes are examples of games that could be implemented using a 2D array.
| 
|
In Lab 5 you will implement a game using a 2D array, so it is important to understand how array elements are accessed and their values are manipulated. We can declare an 2D array of boolean values named gameboard with 8 rows and 8 columns with the Java statement
The number of pairs of square brackets indicates the dimension of the array. In a 2D Java array, the number in the first pair of brackets indicates the row and the second the column. A 2D array is basically a 1D array of 1D arrays, i.e. its rows. The number of rows in our 2D array gameboard is given by gameboard.length. The i-th row of gameboard is the 1D array gameboard[i], and its length (or the number of columns) is gameboard[i].length.
If we want to initialize all values of the array to false, we execute the following statements:
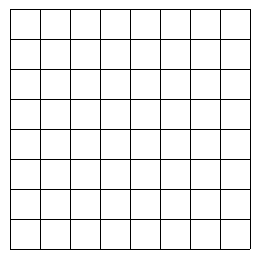
We can visualize our gameboard array as a 8×8 grid of squares, where the top left square corresponds to element gameboard[0][0] and the bottom right square corresponds to element gameboard[7][7].
Color the squares in the grid below corresponding to the elements of gameboard whose values are now true.
For any row r and column c such that 0<r<7 and 0<c<7 we can specify the north, south, east and west neighbors of element gameboard[r][c] as follows:
| gameboard[r-1][c] | (north neighbor) |
| gameboard[r+1][c] | (south neighbor) |
| gameboard[r][c-1] | (west neighbor) |
| gameboard[r][c+1] | (east neighbor) |