Tree Diameter
The function below returns the diameter of a tree. A tree's diameter is
defined after the function. Write a recurrence for this function and
solve it yielding the running time using big-Oh in terms of the number
of nodes in a tree.
int diameter(Tree * t)
// post: return diameter of t
{
if (t == 0) return 0;
int lheight = height(tree->left);
int rheight = height(tree->right);
int ldiameter = diameter(tree->left);
int rdiameter = diameter(tree->right);
return max(lheight + rheight + 1,
max(ldiameter,rdiameter));
}
The following function returns the height of a tree (the number
of nodes on the longest root-to-leaf path).
int height(Tree * t)
// postcondition: returns height of tree with root t
{
if (t == 0)
{
return 0;
}
else
{
return 1 + max(height(t->left),height(t->right));
}
}
where the function max returns the largest of its two integer
parameters.
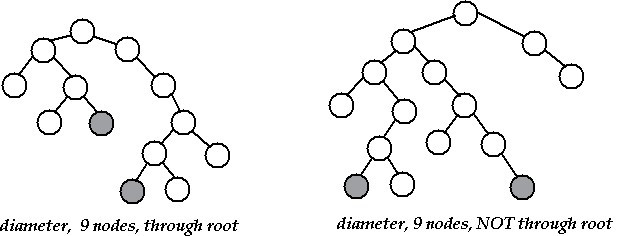
The diameter of a tree (sometimes called the width) is the number
of nodes on the longest path between two leaves in the tree. The
diagram below shows two trees each with diameter nine, the leaves that
form the ends of a longest path are shaded (note that there is more than
one path in each tree of length nine, but no path longer than nine nodes).
The diameter of a tree T
is the largest of the
following quantities:
- the diameter of T's left subtree
- the diameter of T's right subtree
- the longest path between leaves that goes through the root of T
(this can be computed from the heights of the subtrees of T)
Owen L. Astrachan
Last modified: Sun Mar 19 22:09:31 EST 2000

