Directions for setting up Anaconda Python and PyCharm IDE
These directions will guide you through the installation of Python using Anaconda, the installation of the PyCharm IDE, and the creation of a “Hello World!” project in PyCharm.
Contents
For new Anaconda and PyCharm users
- Installing Anaconda and Python
- Creating a Conda environment for COMPSCI 260
- Installing PyCharm
- Creating and running a new Python project in PyCharm
- Opening and editing an existing Python project in PyCharm
For existing Anaconda and PyCharm users
Installing Python 3.11
For this course we will be using Python 3.11. These instructions will be written to reflect the version of Python 3.11 that comes with Anaconda, which at the time of writing is 3.11.5 (the most recent version is 3.11.7, but the differences are small and any Python version 3.11.5 or later should be fine).
We will be installing Python 3.11 using Conda, an open-source package manager that creates and manages Python environments on your computer.
Conda is included in an installation of Anaconda, an open-source Python/R data science platform. Conda can alternatively be installed with Miniconda, a lightweight Python wrapper of Conda. These directions will walk you through an installation using Anaconda, which is easier and more straightfoward.
1. Install Python 3.11 using Anaconda
Download the Anaconda Python 3.11 installer for your operating system here.
Depending on your platform, the instructions to install Anaconda will be graphical or command-line; whichever method you prefer is fine as long as it compatible with your system.
- Windows: Use the 64-bit Graphical Installer (if you have an old version of Windows that is 32-bit, please let us know)
- macOS: Choose the Graphical or Command Line installer that matches your operating system architecture (Intel or Apple Silicon)
- Linux: Choose the Installer that matches your operating system architecture (e.g., x86 or Power8/9)
2. Verify Conda successfully installed
Once installed, open the Terminal (Mac) or Anaconda Prompt (Windows) and test that Anaconda successfully installed Conda by entering the command conda --version. Your terminal output should look similar to the following
(base) $ conda --version
conda 23.11.0
The (base) indicates the current Python environment is currently set to the default base environment installed with Anaconda/Conda, which means that the current Python version should already be Python 3.11. We can check this with the command python --version:
(base) $ python --version
Python 3.11.5
Next, check that the Python interpreter in your path is the one installed by Anaconda using the command which python (Mac):
(base) $ which python
/Users/compsci260/anaconda3/bin/python
or use the command where python (Windows):
(base) C:\Users\compsci260\> where python
C:\Users\compsci260\Anaconda3\python.exe
Either way, you should confirm that the Python interpreter is the one installed by Anaconda. Note that if you used the GUI installer on Mac, the path might be a little different: /Users/compsci260/opt/anaconda3/bin/python.
Creating a Conda environment for COMPSCI 260
Within this (base) environment of Python, we are ready to write and interpret Python code. However, for practical reasons, we will want to create a new environment specifically for this course. Create a Conda environment named compsci260 using the conda create command.
conda create --name compsci260 python=3.11
You will be prompted to install packages into this environment. Confirm and proceed by entering y.
Verify that your new Conda environment has been installed by listing all the available Conda environments using the command conda env list:
(base) $ conda env list
# conda environments:
#
base * /Users/compsci260/anaconda3
compsci260 /Users/compsci260/anaconda3/envs/compsci260
This output shows that we’ve successfully created the compsci260 environment, but the asterisk indicates that the base environment is still active. We can switch to the compsci260 environment using the command conda activate compsci260.
(base) $ conda activate compsci260
(compsci260) $
Note that the command line prompt has changed to indicate the new active environment. You can always switch back to the base environment using the command conda deactivate.
In subsequent sections, we will show you how to integrate your compsci260 environment into Python projects within PyCharm.
Installing PyCharm
Though students may use whichever IDE they are comfortable with, we recommend (and provide instructions and support for) the PyCharm IDE from the company JetBrains.
Decide if you want to use PyCharm Community Edition or Professional
PyCharm Community Edition is the default recommendation for this class as it is smaller and simpler. PyCharm Professional is larger and more complex, providing additional features that are not needed for this class: profiler, scientific packages, more development frameworks, and web development integration. That said, students with an .edu email address can obtain a free license for PyCharm Professional, so if you're serious about Python development and have the space on your machine, feel free to choose it. The link to apply for a free license for the Professional Edition is available here.
Download PyCharm
Download and install the edition of PyCharm you chose in the previous step (Community Edition by default, or Professional if you obtained a license for it) that matches your operating system; if you have a Mac, you will need to choose either Intel or Apple Silicon, depending on your processor.
Creating and running a new Python project in PyCharm
Open the new installation of PyCharm and select New Project:
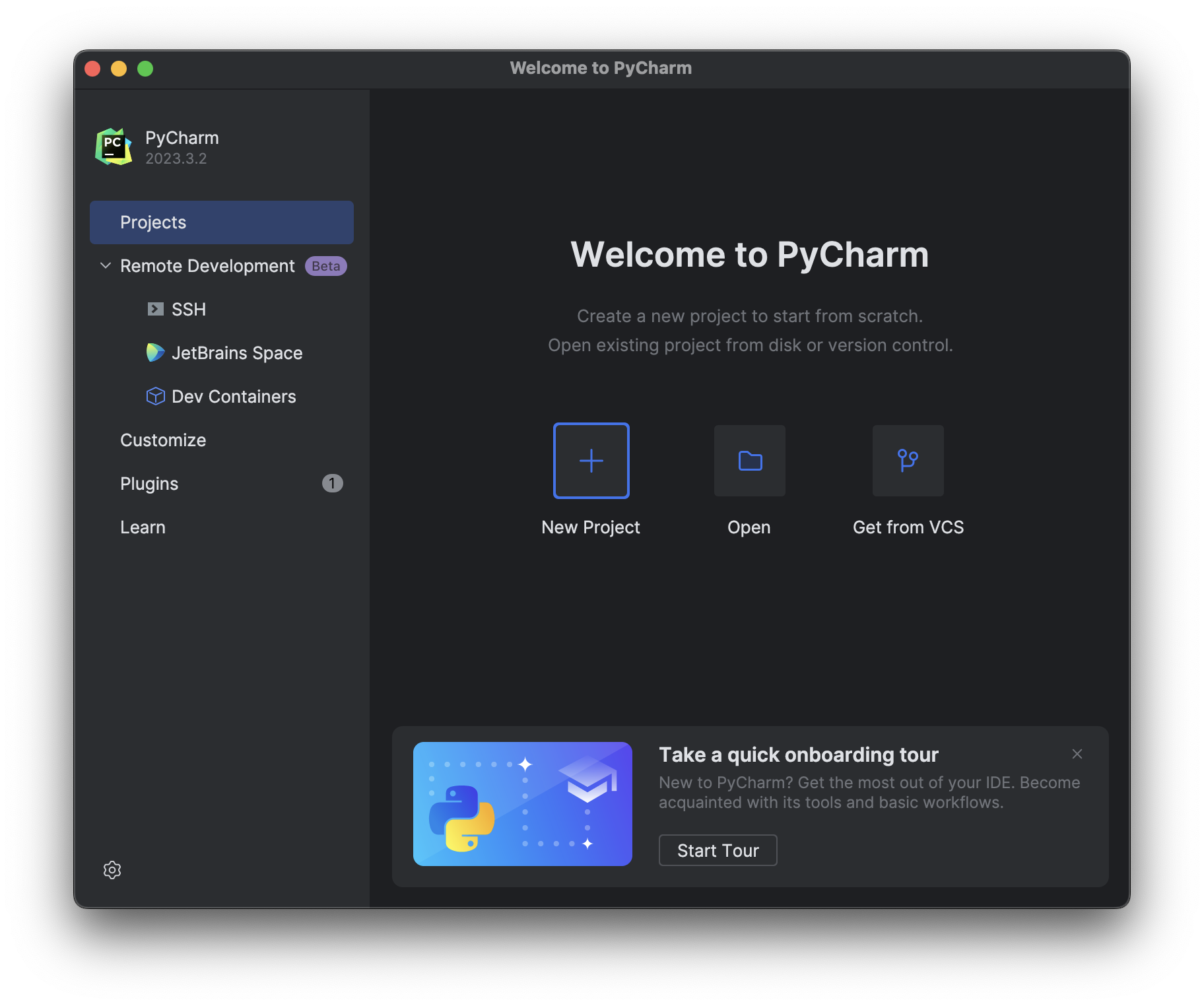
Select Pure Python project and specify a location to create the project. In this example we chose to create a directory named HelloWorld and also check the box to create a main.py script.
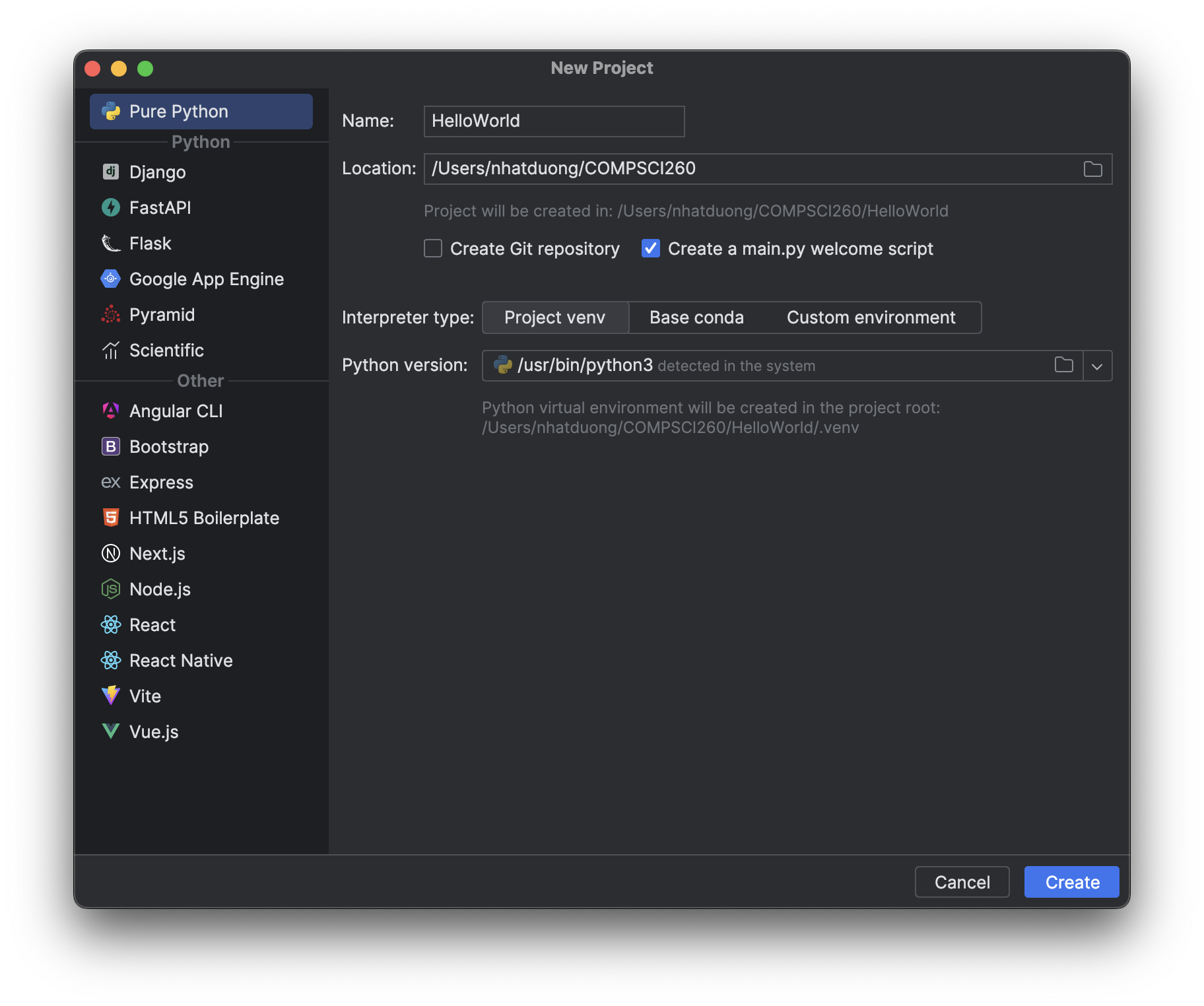
Next, we will need to setup the project to use our Conda environment’s Python interpreter. Select Custom environment and then click the Select existing button:
For "Type", select Conda from the drop down menu. Next, make sure that the "Path to conda" is the path to your conda. It should be something like /Users/your_name/anaconda3/bin/conda. For "Environment", select compsci260 which you created above.

Tip: If you can’t find the path to your conda, activate the environment in a terminal using conda
activate compsci260 and find the python executable path with which python (Mac) or where
python (Windows). From there, your conda path would be the same as your python but just replace python with conda
Now create a new Python file in the project by right-clicking the HelloWorld project, selecting New and Python File. Call this file hello.py.
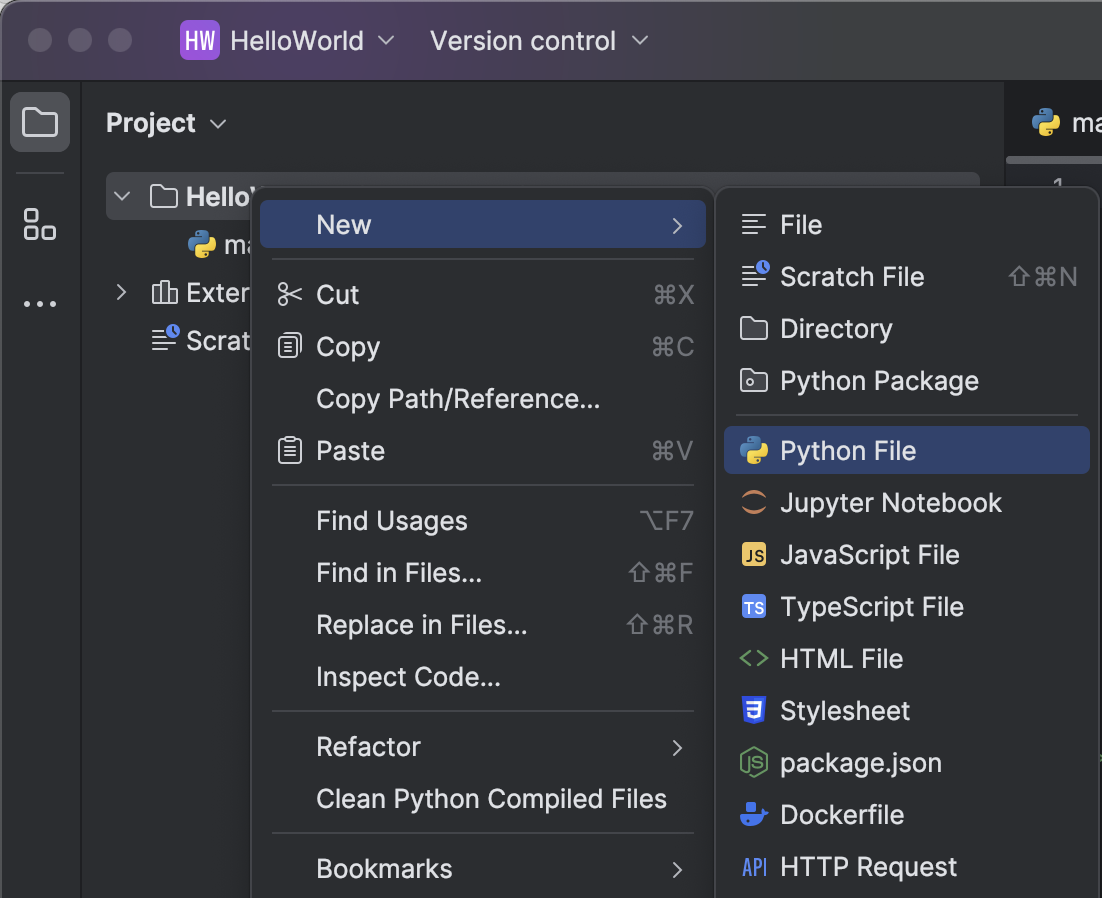
In the body of the file, type:
print("Hello World!")
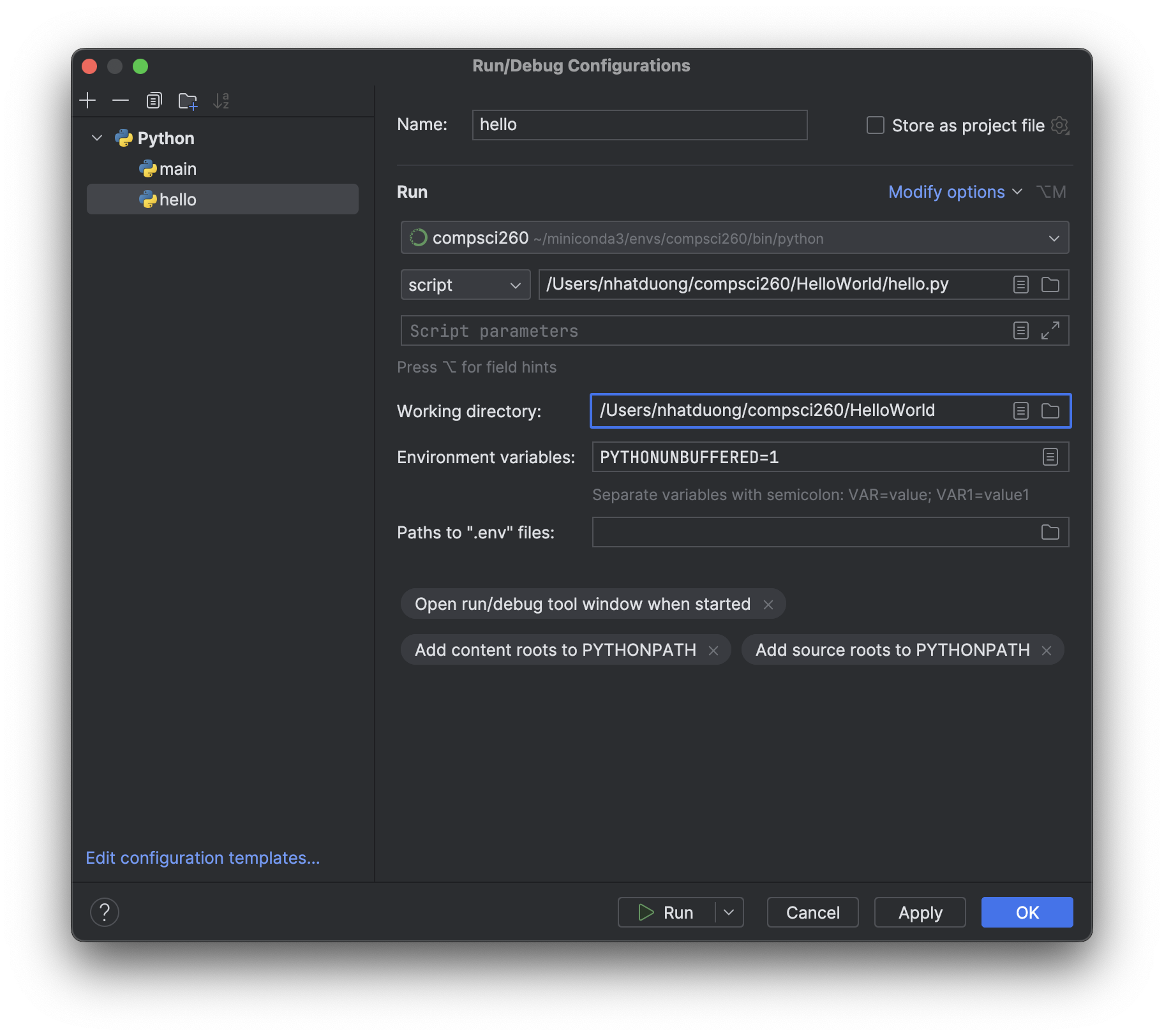
Before we can run, we need setup a run configuration to define how we will run the project. From the menu, select Run -> Edit Configurations:

Select the + sign (top left corner) and add a new Python run configuration. Make sure that your compsci260 environment is selected. In the script path, navigate to the hello.py file we just created. Make sure that the "Working directory" is where you saved your HelloWorld project. When that's all set, select OK.
In the menu, select Run -> Run 'hello'. The Python script will execute and the console should output:
/Users/compsci260/anaconda3/envs/compsci260/bin/python /Users/compsci260/HelloWorld/hello.py
Hello World!
Process finished with exit code 0
Congratulations! You’ve run your first Python project in PyCharm using your Conda environment for this class.
Opening and editing an existing Python project in PyCharm
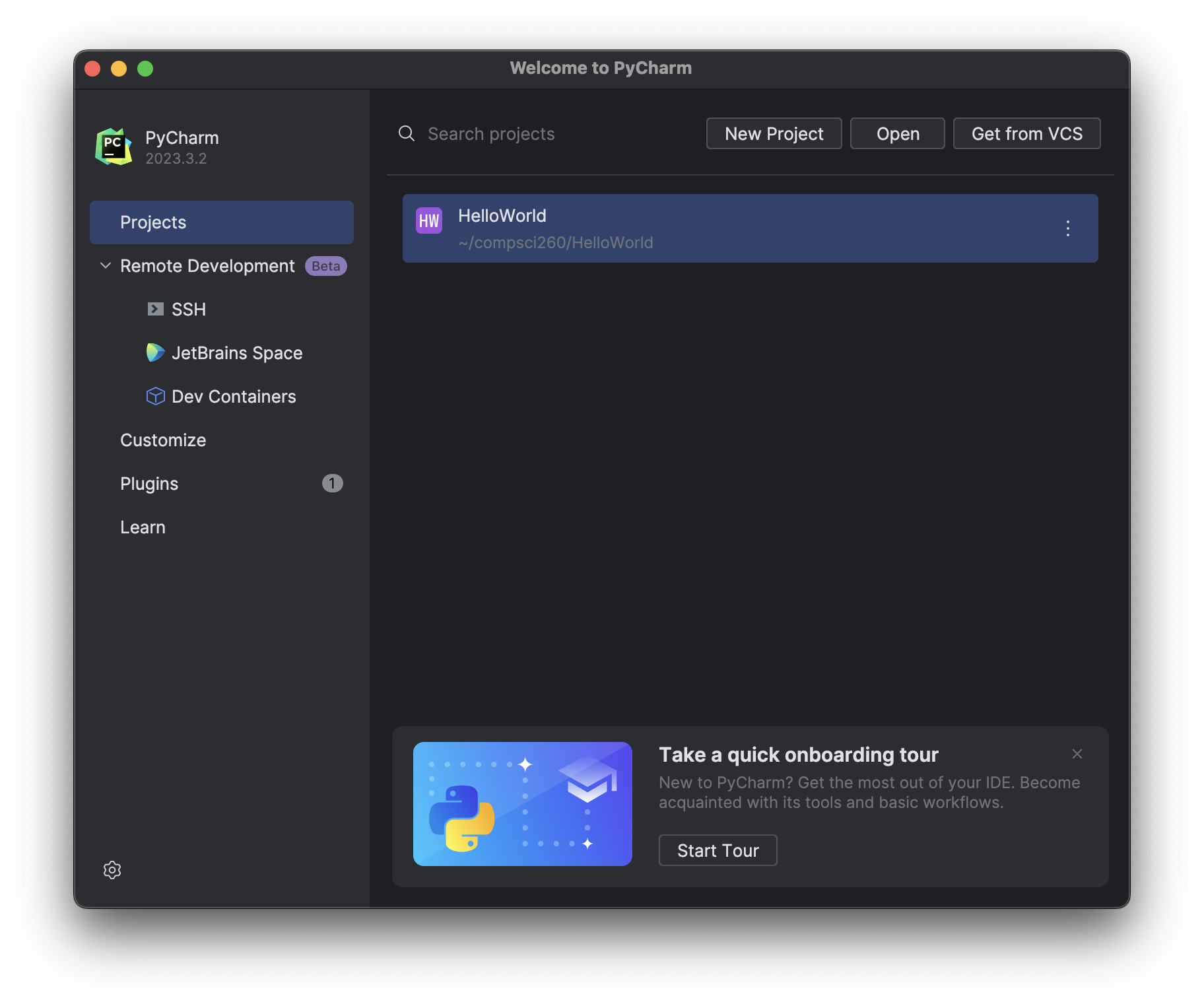
Opening an existing Python project is very similar to creating a New Project. Close any open PyCharm windows and the Welcome to PyCharm window should appear.

Select Open and navigate to an existing projects directory and select Open. Note: Ensure you are opening the directory itself rather than a specific Python file in the directory.
If this is the first time the project has been opened in PyCharm, we need set up a run configuration to define how we will run the project. From the menu, select Run -> Edit Configurations:

Select the + sign (top left corner) and add a new Python run configuration. Make sure that your compsci260 environment is selected. In the script path, navigate to the hello.py we just created. Make sure that Working Directory is where you saved your HelloWorld project. Select OK.

In the menu, select Run -> Run 'hello'. The Python script will execute and the console should output:
/Users/compsci260/anaconda3/envs/compsci260/bin/python /Users/compsci260/HelloWorld/hello.py
Hello World!
Process finished with exit code 0
Congratulations! You’ve open and run an existing Python project in PyCharm using a Conda environment.
Updating Anaconda
If you already have a fairly recent installation of Anaconda or Miniconda, you do not need to uninstall and then reinstall it. Just open up Terminal (Mac) or Anaconda Prompt (Windows) and then type conda update -n base -c defaults conda and then y to install the latest version of conda. After this you should have conda version 23.11.0, which you can test by entering the command conda --version. Your terminal output should look similar to the following:
(base) $ conda --version
conda 23.11.0
The (base) indicates the current Python environment is currently set to the base environment.
Next, if you don't already have Python version 3.11, you will need to install it by typing conda install python=3.11 and then y. That should give you the latest version of Python 3.11, which is likely 3.11.7.
To verify that your current Python version is now set to Python 3.11, use the command python --version:
(base) $ python --version
Python 3.11.7
Finally, confirm that the Python interpreter in your path is the one installed by Anaconda using the command which python (Mac):
(base) $ which python
/Users/compsci260/anaconda3/bin/python
or use the command where python (Windows):
(base) C:\Users\compsci260\> where python
C:\Users\compsci260\Anaconda3\python.exe
Updating PyCharm
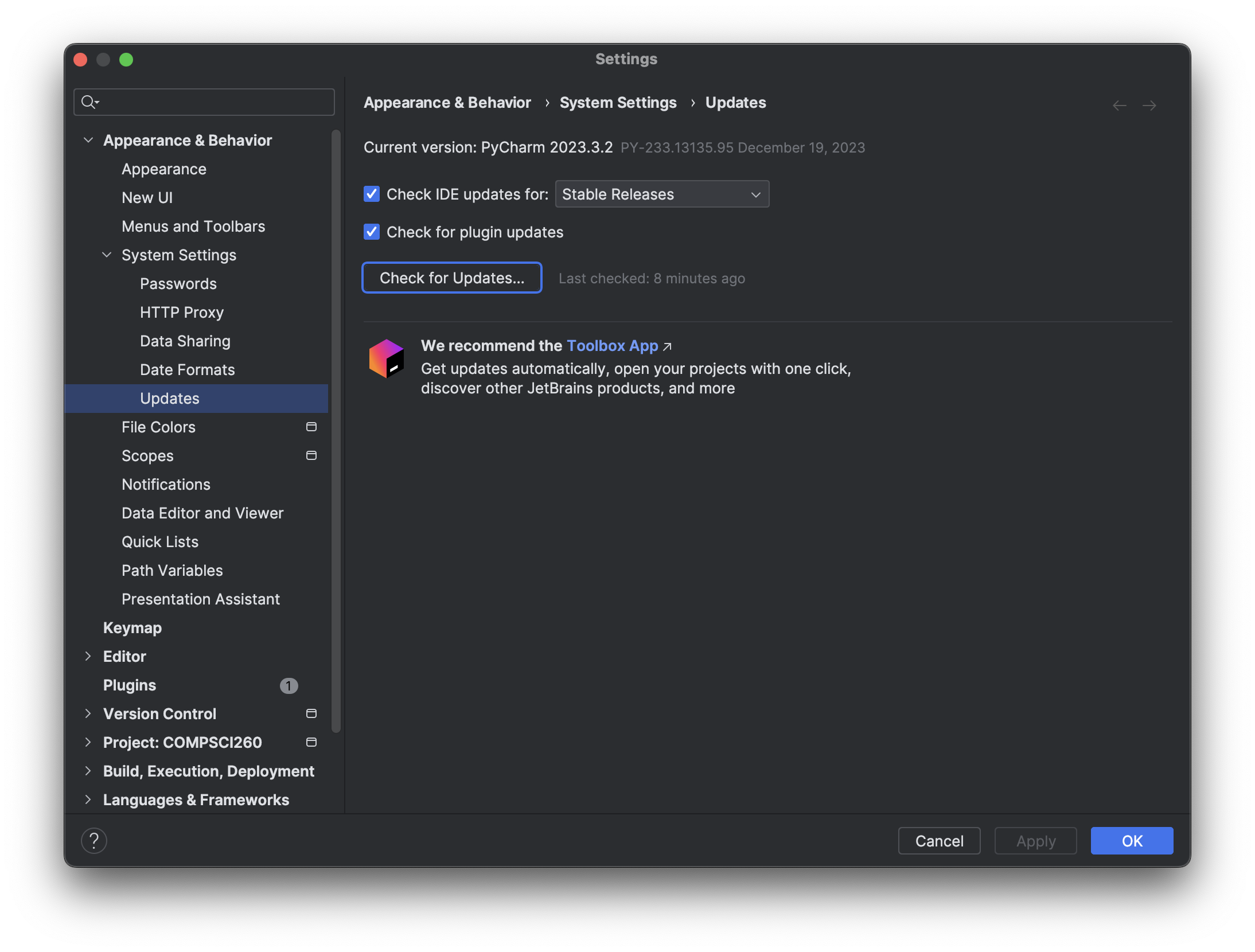
Open up your existing PyCharm application and navigate to Settings | Appearance & Behavior | System Settings | Updates; on a Mac, you'll find the Settings option under PyCharm in the menubar; on a Windows machine, it will be in the File menu. There, you should be able to update to the next version of PyCharm. Keep repeating this step until you have PyCharm version 2023.3.2.
Once your Anaconda, Python, and PyCharm are all updated, return to the following steps to ensure that your Python projects in PyCharm are configured to run using the Python interpreter installed by Anaconda.