debugging a project
Oftentimes
programs will not function as expected because the
programmer possibly forgot to initialize a variable, made a mistake
setting conditions such that a loop will never terminate, or did not
account for a method call that returns null. Fixing these errors takes
very little time, but finding the error in the code can be a very
difficult task. The concept of debugging aims at speeding up the
locating process of programming flaws.
Debugging
allows the programmer to set break points in the code.
When executing the program in debug mode, Eclipse will run the program
normally, but it will pause (not stop) execution at the first break
point. The programmer can then observe the state of all currently
declared variables. Moreover, the programmer can step through the code
to see how the next instructions will affect the variables. Execution
can be resumed and the program will either terminate normally, or
Eclipse will stop at the next break point it detects.
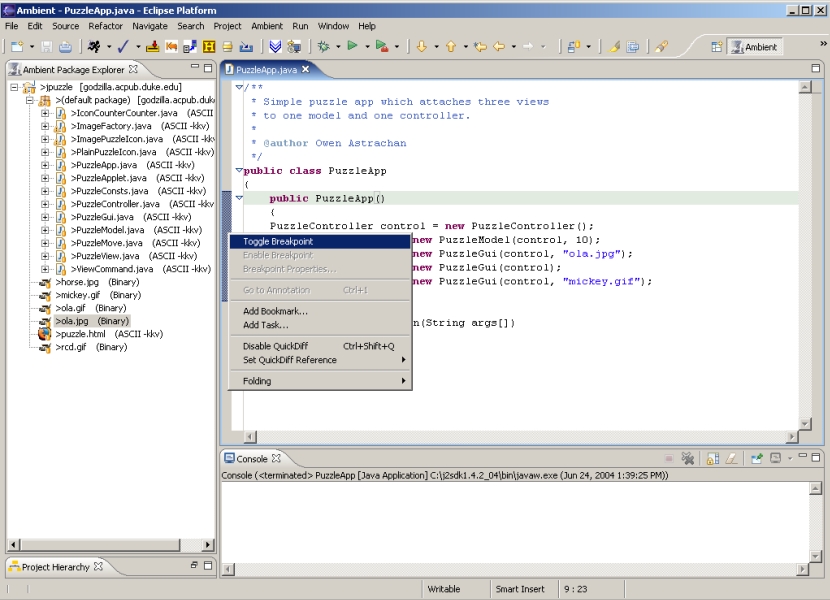
setting break points
In order to
set a break point, simply right click on the gray margin
to the left of the line of code in the editor. A small context menu
should open, which will allow you to add a break point. To start the
debugging process go to Run > Debug As > Java Application.
The Debugging perspective
Once you have
started the debugging process, Eclipse will switch to
the debugging perspective. This perspective may seem complex and
confusing at the beginning, but this should not discourage you from
using it. Here are the key elements you should be familiar with:
The most
interesting part of the debug
view is the toolbar (marked in blue).
- Resume -
will result in normal execution of the program until the
next break point
- Suspend -
will pause execution and allow you to view state of
variables
- Terminate -
will terminate execution of the program
- Step Into -
if you are at a method call (e.g., Math.pow(200) )
and you would like to know what the method does you should use Step Into
- Step Over -
if you only care about what a method will return or
how it will change your variables use Step
Over
- Step Return
- will finish the method you are currently in and
return to the point the method was called from
These six
buttons will allow you to navigate the program execution
while you can observe what values methods return and how the affect
your
variables.
- Variables
view (marked in blue on the right side)
This view
simply shows all variables that are currently defined in the context of
your program.
You will see
the program line the
debugger is currently at. If the execution of your program takes you to
a different class, Eclipse will open up the corresponding .java file
automatically.
- Console
view (bottom blue rectangle)
Much like the
console view in the
Ambient perspective it will show output of the program that's running
and
allow for user input.
|