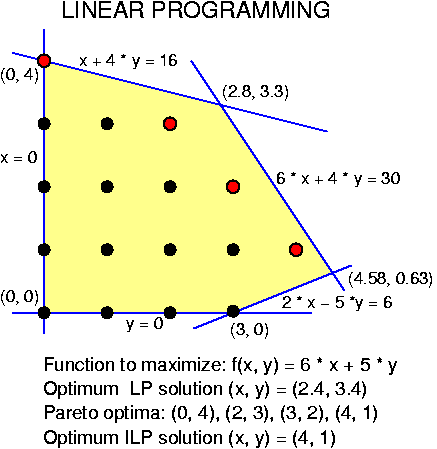
image taken from http://users.informatik.uni-halle.de/~jopsi/drand04/linear_programming.gif

| Date | Topic | Materials |
| Introduction. Examples of linear and integer programs. Solution by graphical inspection. Linear programs in abstract form. | Lecture notes 1. | |
| Applications. Maximum flow. Combinatorial (reverse) auctions. Zero-sum games. Markov decision processes. (Kemeny) rank aggregation. Sudoku. | Lecture notes 2. | |
| Using the GNU Linear Programming Kit and its modeling language. | Lecture notes 3. Homework 1. |
|
| Duality. Weak duality, strong duality, complementary slackness. | Lecture notes 4. | |
| Duality in applications. | Lecture notes 5. | |
| A direct proof of strong duality. | ||
| The simplex algorithm. | Lecture notes ?. | |
| Network flow problems. | Lecture notes ?. | |
| Constraint and column generation. The cutting stock problem. | Lecture notes ?. | |
| The ellipsoid algorithm. Polynomial-time separation oracles. | MIT lecture notes one and two. (For the midterm, you do not need to know things that we didn't cover in class.) | |
| An illustrative example: the core and network flows. | Lecture notes ?. | |
| Branch and bound. | Lecture notes ?. | |
| Valid inequalities/cutting planes. | Lecture notes ?. |